Computer is an electronics device which can perform simple to complex arithmetical calculation as well as logical operation, it is called Computer. computer is a machine that can perform several different functions. You can decide what the computer should do for you-that is you can program your computer to do your job, the way you want it done.
Computers are getting more and more advanced every day. They are becoming more powerful, faster and easier to work with. Computer programs are getting lengthier and more sophisticated. They help us get more out of the machine. Today computers can do what we could never imagined a few years ago.
computer is an electronic device that processes data according to a set of instructions or programs. Its primary function is to perform complex calculations and automate repetitive tasks quickly and accurately. In today’s world, computers play an essential role in various sectors, including education, healthcare, entertainment, and communication. Whether it’s for personal use, professional work, or industrial applications, computers have revolutionized how we interact with information and perform daily tasks.
At its core, a computer comprises several key components: the central processing unit (CPU), memory, storage devices, input/output devices, and software. The CPU is often referred to as the brain of the computer, as it executes instructions from the programs. Memory, or RAM (Random Access Memory), temporarily stores data that the CPU needs to access quickly. Meanwhile, storage devices such as hard drives or SSDs hold data and software permanently. Input devices like keyboards and mice allow users to interact with the computer, while output devices such as monitors and printers display or print the results.

The term “computer” originally referred to a person who performed calculations, but over time, it became associated with the machines that could do this faster and more efficiently. Modern computers are classified into various types, such as desktops, laptops, tablets, and servers. Each of these serves specific purposes. For example, laptops are portable computers designed for mobility, while servers are more powerful machines that store and manage data for networks or websites.
Computers operate through a combination of hardware and software. Hardware refers to the physical components, while software consists of the programs and applications that run on the machine. The operating system, such as Windows, macOS, or Linux, serves as the interface between the hardware and user, managing resources and providing an environment for other software to function.
The versatility of computers has led to their widespread adoption in almost every aspect of life. They are indispensable tools for tasks such as word processing, web browsing, programming, and gaming. Additionally, with advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, computers are becoming smarter and capable of performing tasks that once required human intelligence.
FULL FORM OF COMPUTER
C-COMMONLY
O-OPERATED
M-MACHINE
P-PERMANENTLY
U-USED IN
T-TRADE
E-EDUCATION &
R-RESEARCH
MAINLY COMPUTER MADE IN 4 PARTS:
a) MONITOR/VDU(Visual Display Unit):
It’s an Output Device, Any Dot stay on Desktop it is called Pixel. Mainly two types of Pixel as Dot Pixel and Square Pixel. a line crate on multiple dots. Image quality depends on Pixel, we know that combined of pixel is Resolution. Multiple icon stay on desktop as Computer, Recycle Bin, Network, Control panel, any software shortcut keys. Todays available monitor remaining in market as CRT-Cathode Ray Tube, LED-Light Emitting Diode, LCD-Liquid Crystal Display, TFT-Thin Film Transistor.
b) MOUSE/GUI(Graphical User Interface):
It’s an input device. it is important part of graphics design students. creating design, photo editing, Animation etc. work with mouse. click on any option with mouse from user. 3 button in mouse as Left button, Right button and Scroll button. Left hand side button called Left button. quickly 2times click on left button it is called Double click. Right hand side button called Right button. Middle button called Scroll button. Scroll button work page up and down. Mainly used mouse in school college, institute, industry as Ball Mouse, Optical Mouse, Wireless Mouse.
c) KEYBOARD/CUI(Character User Interface):
It’s an input device. it is important part for data entry operator. Keyboard has multiple keys. Every keys has own has different values, it is called ASCII Key(AMERICAN STANDARD CODE FOR INFORMATION INTERCHANGE). Here remaining keyboard as Normal Keyboard(QWERT), Multimedia Keyboard & Wireless Keyboard.
- Alphabetic Keys: A,B,C,D,E……………………..Z and a,b,c,d……z
- Numeric Keys: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
- Functional Keys: F1, F2,F3,F4,F5,F6,F7,F8,F9,F10,F11,F12
- Special Keys : Ctrl, Alt, Shift, Delete, Insert, Home, End, Print Screen, Page Up, Page Down etc.
- Navigation Keys : Top Arrow, Down Arrow, Left Arrow, Right Arrow
- Familiar Keys Identity:
- ! – Exclamation
- @ – At the rate of
- # – Hash
- $ – Dollar
- % – Modulus or percentage
- ^ – Caret or Power
- & – am percent or (and sign)
- * – Multiplication
- / – Division
- ( – first backed open
- ) – first backed close
- _ – underscore
- + – Addition
- – – Subtraction
- { – Curly bracket open
- } – Curly bracket close
- [ – Square bracket open
- ] – Square bracket close
- \ – Back slash
- / – Front Slash
d) CPU(Central Processing Unit):
It’s a processing device and also called mother of computer. In built CPU given the below list as
CABINET WITH SMPS: Switch Mode Power Supply
MOTHER BOARD: P-iv, Intel, Asus, Giga Byte, Zebronics etc.
PROCESSOR: Intel
COOLING FAN: Zebronics, Intel
RAM: Random Access Memory(DDR2, DDR3,DDR4)
ROM: Read only Memory(LG, HP, SUMSANG)
HARD DISK/SSD CARD: SATA, PATA, 1 TB, 500 GB
GRAPHICS CARD: VFX
FLOPPY DISK: 1.44 MB DATA
HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF COMPUTERS
2400 BCE: Abacus : It is the earliest known computing device. It consists of beads strung on rows of wires or rods. You can
calculate and perform arithmetic operation by moving these beads in a particular pattern.

Abacus
1617 AD: Napier’s Bones : John Napier invented a system of moveable rods based on logarithms which was able to multiply, divide and calculate square and cube roots.
1622 : Slide rule : It was mainly used for multiplication and division. It was also used for functions such as roots, logarithms and trigonometry, but not normally used for addition and subtraction.
1642 : Pascaline : Blaise Pascal, a nineteen year old boy invented a calculating machine called Pascaline. This device could add, subtract and multiply. He did this to help his father who was an accountant.
1801 : Punched Cards : Joseph-Marie Jacquard developed a loom in which punched cards were used. These punched cards controlled the different patterns being woven. The series of cards could be changed to alter the design, without changing the mechanical design of the loom. Early digital computers used punched cards as a medium to input both program and data.
1833 : Difference Engine : Charles Babbage designed the Difference Engine which used Jacquard’s punched cards for its program storage.
1834 : Analytical Engine : Charles Babbage invented the Analytical Engine. It had all the essential features which are found in modern digital computer. It was programmable using punched cards. It could store the data in a separate engine called ‘Mill` where all arithmetic processing was performed. But Babbage was far ahead of his time and technology needed to make the analytical Engine was not available at that time. Only part of a trial piece was constructed before Babbage died.
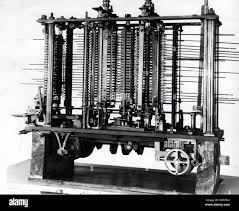
Analytical Engine
1890 : Herman Hollerith designed a system to record census data using punched cards. He started a company which later became IBM.
1946 : ENAIC (Electrical Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the first large general-purpose electronic computer to be made operational. It was made in USA by John Presper Eckert and John William Mauchly. It worked on vacuum tubes and filled an entire room. This was the first generation computer.
1947 : Transistor : Bradford, Bardeen and Brattain invented the transistor. It could perform the same function as the valve but was smaller, cheaper, faster, more reliable and consumed less electricity.
1951 : UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) : It was the first commercial computer. It was developed by John Prester Eckert and John William Mauchly.
1954 : Second generation computers : Bell Lab introduced the first computer using transistors instead of valves.
1958 : Integrated Circuits (ICs) : The invention of ICs brought further reduction in size and increase in speed of computers.
1960s : Third generation computers : Many smaller computers were made using integrated circuits. Simultaneously, a lot of research was going on in the field of robotics. Computer-aided design (CAD) and word processing activities started to catch up.
1969 : First network known as ARPANET was established.
1970s : First Automated Teller Machine (ATM) was introduced.
Invention of microprocessor : With the coming of microprocessor, a whole range of smaller and more powerful computers got made. These computers were the fourth generation computers.
1981 :IBM introduced the first personal computer (PC). MS-DOS operating system was introduced by Microsoft.
1983 : Apple Lisa computer : It was the first home computer with a GUI (Graphical User Interface).
1985 : Microsoft Windows 1.0 was released.
Since then, Computer is an electronics device & getting more and more advanced every day.computers have became smaller and smaller, and more and more powerful. Computers with sound, graphic and animation capabilities have flooded workplaces and homes today. Researchers are developing devices that respond to human languages, and devices in the market already have the capability of voice recognition. A lot of research is going on in the development of artificial intelligence.
ADVANTAGES OF COMPUTER ( COMPUTER CHARACTERISTICS)
- Speed : A computer can follow one instruction at a time. Hence the speed of a computer is measured by the number of instructions the microprocessor can carry out every second. This is measured in Million Instructions Per Second (MIPS). The microprocessors used in desktops and laptops may have speeds of 1,00,000 MIPS or more. The supercomputers of today can carry out billions of instructions per second. However, the speed of supercomputers is measured in FLOPS (Floating-Point Operations Per Second) rather than MIPS. (Computers are much faster as compared to human beings. A computer can perform millions of calculations in fraction of seconds which human beings might take hours or days to perform.)
- Memory/Storage :Computers can store large amounts of data in small physical spaces. This is called computer memory. Memory is the storing place for both data and instructions; it could be located inside the computer (internal) or outside (external). Memory is further classified into primary and secondary memory. A flash memory (pen drive) can store 4 GB to 64 GB of information whereas bubble memories store millions of bits per square centimeter of space.
- Deligence : Computers are not prone to tiredness. They are not affected by boredom or fatigue. They are reliable and trustworthy gadgets for the human beings.
- Versatility :Computers can perform a variety of jobs and can perform repetitive jobs efficiently. They can do labour problems and perform hazardous jobs in hostile environment. They can do work where human may not. The computers can work with different types of data and information like graphics, audio, video, characters etc.
- Accuracy : Computer performs calculations with speed and accuracy. It performs comparisons very accurately if the hardware does not malfunction.
SOME WEAKNESSES OF COMPUTER ( DISADVANTAGES OF COMPUTER )
- Computers cannot take decision on their own. They are machines. They do not possess thinking power like human beings.
- Computers are deaf and dumb machines. They have to be told what to do and what not.
- If a computer commits an error on any statement, it repeats the error when the statement is encountered. In other words, a computer is a non-heuristic machine.
BASIC APPLICATIONS OF COMPUTER ( AREAS OF APPLICATION )
- Education (Training & Teaching, Online Class, details of fees, marks and attendance, admission, maintaining accounts of the school, College, Institute)
- Communication ( e-mails, video-conference meeting, chat)
- Government (The income tax, sales tax, VAT, GST, TDS)
- Computers at homes (Play game, send e-mail, video chat, write thesis, listening to music, office work in leisure time.)
- Business (Accounts in banks, train & flight reservation, Online Purchase Order)
- Science and research (experiment, design, develop projects on CAD & CAE)
- Movies and Music (amazing effects, The Matrix, Titanic movies give effects)
- Medicine and health (diagnosing the illness of patients, curing ailments and surgery, heart disease-pacemaker)
- Law (the police can trace the criminals by the DNA fingerprints, license number, traffic police use speed cameras to check over-speeding)
- Armed forces (Military, Missiles, weather conditions)
COMPUTER CLASSIFICATION
Computers can be classified into different categories depending upon their physical size, processing speed, storage capacity, cost and ability to get connected to other computers and input or output devices.

Laptop and tablet computers are portable computers that work on rechargeable batteries.
Personal computers (PCs) are the small computers you can see in schools, homes and in most offices. They are called microcomputers.
Minicomputers are more powerful than PCs. Several people can use a minicomputer at the same time. They are normally used for processing large data and for industrial applications.
Mainframe computers are even more powerful computers that have high-storage capacities. They are used in large commercial and government organizations.
Supercomputers are the fastest of all computers. They are used for large applications that require complex scientific calculations.
HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF COMPUTERS:
Question 1. Which was the computer conceived by Babbage?
Question 2. Who designed the first electronics computer – ENIAC?
Question 3. First generation computers are characterized by
Question 4. Second generation computers are characterized by
Question 5. Third generation computers are characterized by
Question 6. Four generation computers are characterized by
Question 7. Fifth generation computers are characterized by
Question 8. How many types of Main memory?
Question 9. Which unit holds data permanently?
Question 10. Which super computer is developed by Indian Scientists?
Functioning of CPU :
1. The data/information is received by the Control Unit from the Input devices.
2. Then that data/information is sent to the Memory Unit for storing it.
3. The Control Unit sends the data/information from the Memory Unit to the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
4. ALU is responsible for all the arithmetical operations like the multiplication, division, addition etc. as well as comparison.
5. The processed information from the ALU is then transferred to memory for temporary storage by the Control Unit before sending it can be sent on monitor etc.
INPUT UNIT :
This unit helps to read the raw data or program required to solve a problem. The program contains the instructions about what has to be done with the data. This units builds an interface between a user and a machine.
The following are the input units:
Keyboard, Mouse, MICR, Light Pen, Joystick, Scanner, Punch Card, Punch Card Reader, Bar Code Reader, Optical Mark Reader, Optical Character Reader, Graphic Tablet, Sound Synthesizer, Smart Card, Biometric Sensor, Microphone, Digital Camera
OUTPUT UNIT :
These devices are required to deliver results to the user of the computer system. This unit provides a way of machine to man communication.
Some of the popular output units are:
- Monitor or VDU (ii) Printer (iii) Plotter (iv) LCD (v) Speakers
ARITHMETIC AND LOGIC UNIT:
This unit is responsible for all the arithmetic computations and logical operation involves comparisons (>, <, >=, <=, =) etc.
CONTROL UNIT:
As the nervous system controls the functioning of all body parts, control unit is responsible for the movement of data and instructions in and out of the memory and CPU. It is also responsible for the decoding of fetched instructions and determining as to which is desired by the same. The CU also controls the operations of the ALU.There are two types of memories:
Primary Memory (b) Secondary Memory
RANDOM ACCESS MEMORY (RAM)
Syntax : “Doing is the mother of getting”__Sri Sri Thakur

- RAM temporarily hold user contents.
- RAM is also primary storage device.
- RAM is also known as volatile memory.
- For any kind of power failure or if we accidentally switch off PCs, all contents of RAM will erase.
- So contents of RAM are written by user.
- We can say RAM another also a Read/Write memory.
- And also user can manipulate the contents of RAM.
- Different categories of RAM is SDRAM, DDR
READ ONLY MEMORY (ROM)
- The memory we can only read the contents of ROM, but we can’t manipulate the contents of ROM.
- The contents of ROM are static.
- It display some basic system information like configuration of PCs, date & time of manufacturing etc.
- The contents of ROM are written by manufacturer during the time of manufacturing.
- This nature of ROM is also non-volatile memory.
- ROM can be categorized as follows:
- a. PROM b. EPROM c. EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory)
HARD DISK (HDD)
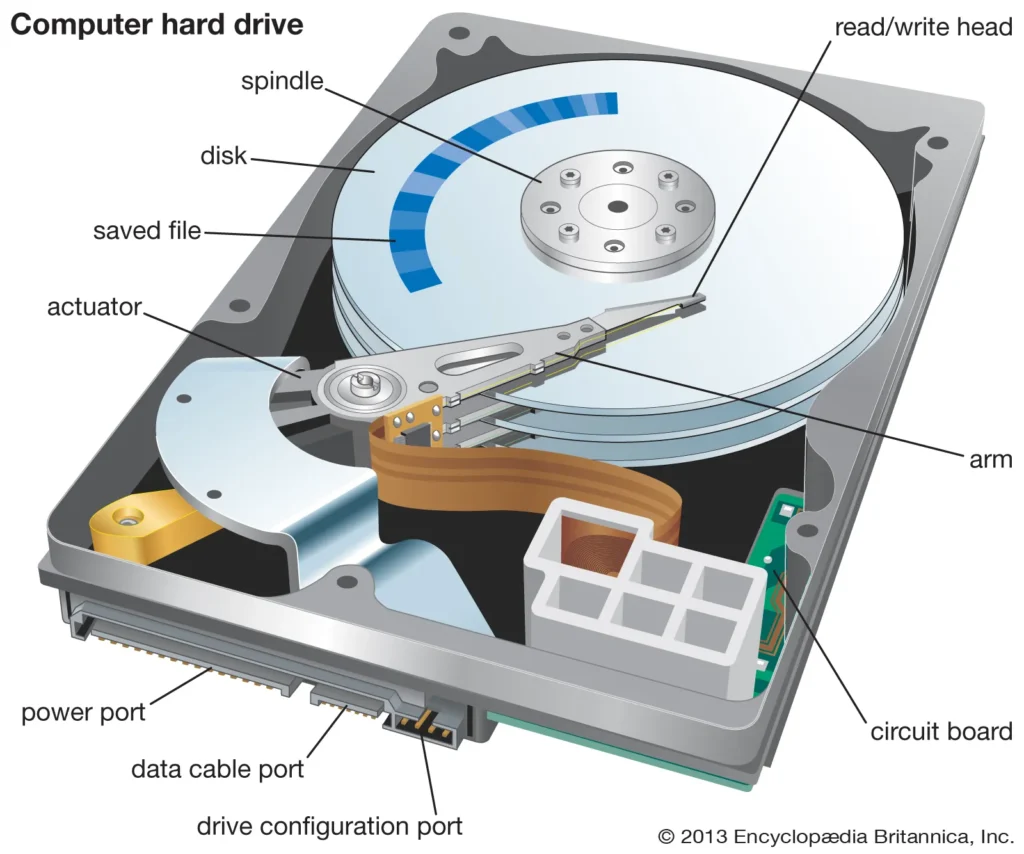
- It can store data permanently, as long as I want.
- It is an electro-magnetic device, which is attached with mother board inside CPU.
- Hard Disk is denoted by C:
- Any Hard Disk we can store large amount of data, generally few GBs or TBs of data.
- So Hard Disk is less prone to damage, because it reside inside CPU, without getting contact of dust, sunlight etc.
FLOPPY DISKS (FDD)
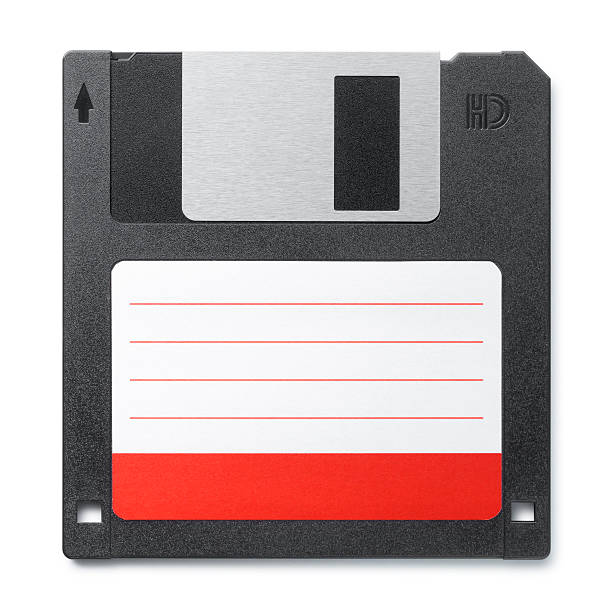

- It is made of flexible plastic which is coated with magnetic-oxide.
- It is Very light weight, thin. We can carry floppy with ourselves anywhere.
- Floppy Disk is denoted by A:
- It can store maximum of 1.44 MB of data.
- This is not reliable because it easily gets damaged by external dust.
- Floppy disks introduced by IBM (International Business Machines) in 1972.
PEN DRIVE :

Pen Drive is often referred to as a jump drive. It is a portable flash memory solution, designed to transport data files from one computer to another. The product can carry audio, video and data files, and is brilliantly simple; all the user has to do is plug the pen drive into a computers USB port, drag and drop the necessary files from the hard drive, remove it and plug it into another machine.
BLU-RAY DISC :
Blu-Ray Disc is an optical disc storage medium designed to supersede the standard DVD format. Its main uses are for storing high-definition video, PlayStation 3 video games, and other data, with up to 25 GB per single layered, and 50 GB per dual layered disc. Although these numbers represent the standard storage for Blu-Ray drives, the specification is open-ended, with the upper theoretical storage limit left unclear.
TOUCH SCREENS :

Computers now have touch screen capability. This means that a person using the computer does not have to type commands using a keyboard. All options appear on the screen as graphic images. You need to touch an image on the screen to select the option. The computer program then decides what to do next. Touch screens are especially useful in areas where the number of options is limited, for example touch screens are great for conducting quizzes, where you have to select one out of three or four possible answers.
AUTOMATIC TELLER MACHINE (ATM) :

You know that computers have penetrated into business and banks in a big way. However, it is only towards the end of the 1990s that computerized automatic teller machines (ATMs) became popular. These machines are programmed to function throughout the day and night. You can walk in at any time of the day or night and withdraw cash from these machines. Such machines can be located far away from the bank itself. They are simple to operate. The user can read the instructions on the machine and push the necessary keys to make a successful transaction. Touch screens are also used in ATMs. HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, State Bank of India and most other banks have a number of ATMs installed in major cities in India.
CARD READER :
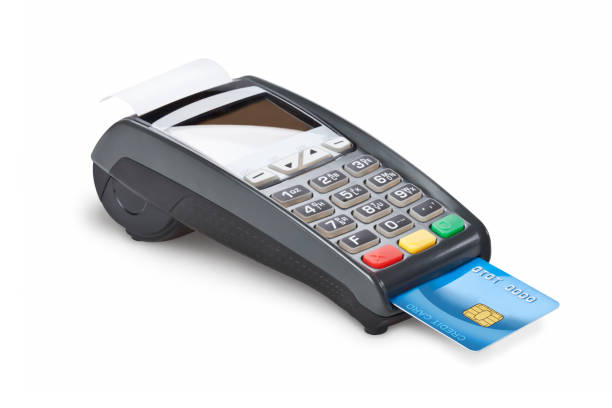

In a credit card or a debit card, data is stored in a magnetic strip. This data does not change. These cards are used for shopping or withdrawal of money from an ATM. The card reader in the ATM machine or the shop reads the information about the purchaser and his/her bank from the card, and sends it to the bank computer. Credit cards and debit cards are also known as electronic money. In a smart card, data is stored in a computer chip. This data can be changed. For example a metro card used instead of buying a ticket for travel on the metro, is a smart card. It will have data about the amount of money stored in it. Every time you undertake a metro trip, the card reader and computer at the station reduce the amount and save the new amount on the card.
UNIT OF MEMORY :
0 or 1 = 1 BIT
4 BITS = 1 NIBBLE
8 BITS = 1 BYTE
1024 BYTES = 1 KILOBYTE (KB)
1024 KILOBYTES = 1 MEGABYTE (MB)
1024 MEGABYTES = 1 GIGABYTE (GB)
1024 GIGABYTES = 1 TERABYTE (TB)
1024 Terabyte = 1 Petabyte
1024 Petabyte = 1 Exabyte
1024 Exabyte = 1 Zettabyte
1024 Zettabyte = 1 Yottabyte
1024 Yottabyte = 1 Brontobyte
1024 Brontobyte = 1 Geopbyte
Geopbyte is the highest memory measurement unit.
OPERATING SYSTEM :
Operating System is a program which helps the computer to run. Without any Operating System no computer can run or even work. It is just like the heart of the computer.
Some examples of operating systems are MS-DOS, MS-WINDOWS, UNIX, LINUX and Ubantu., Windows 10, Windows 11
SOFTWARE :
Software is a collection of set of programs designed to carry out special task such as word processing, database management (data entry, processing and analyzing) etc. By the nature of their functioning, software can be divided into two categories: Application Software and Utility Software.
APPLICATION SOFTWARE :
Software developed to perform specific functions, are called Application software. Application software is now available that can take care of almost all the operations of business such as account, inventory, payroll etc.
e.g. MS-WORD, TALLY, MS-EXCEL etc.
UTILITY SOFTWARE :
The utility software is the program which is helpful and ensures proper and smooth functioning of the system. Utilities are meant to assist the computer in many ways. These utilities might help taking backup of the data, removing old data, recovery of damaged data
ASSEMBLER :
The translator that converts assembly language code to machine language is called the assembler.
COMPILER :
The Language processor is a translator that produces machine or assembly code as output as object code or executable codes then it is called a compiler.
INTERPRETER:
The interpreter is the Language processor that converts the source code into machine language line by line. If the language processor executes the translated program then it is called an interpreter.
SOME OF THE HIGH LEVEL LANGUAGES (HLLS) ARE DESCRIBED BELOW :
- BASIC: It stands for Beginners All Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code. It is very popular language among schools and early learners. It was developed by John Kemeny and Thomas Kurtz in early 60’s. It is very helpful in Developing logic and understanding the programming paradigm.
- COBOL: It stands for Common Business Oriented Language. This language was designed specifically for processing business data such as to develop accounting, payroll or stock management software etc. by CODASYL (Conference on Data System Language) in 1959.
- PASCAL: This language was named after a famous French Mathematician Blaise Pascal who was responsible for the making of Pascal’s Adding Machine. It is a structured programming language and is used for scientific as well as business applications. It is developed by prof Niklaus wirth of Zurich, Switzerland in 1971.
- FORTRAN: It stands for Formula Translation developed by John Backers. This language was designed to simplify and speed up the complex scientific and mathematical applications.
- LOGO: This language was developed by Seymour Pappert. It is a wonderful language to teach children logical analysis, with the help of Turtle and Graphics.
- C: C is a general purpose structured programming language. The compiler of C is commonly available for the computers of all sizes. It was the modified version of two earlier languages, called BCPL and B, which were also developed at Bell laboratories.
- C++: C++ is an object-oriented programming language, originally known as ‘C’ with classes. It was developed by Dr. Brarne Stroustrup at AT&T’s Bell Labs in the early 1998s.
- JAVA: Java was developed by James Gosling, the chief programmer of Sun Microsystems. It is an object-oriented programming language. It was developed after C++. Java is the most popular because it is used for Internet programming.
BOOTING :
When we start the computer then for few minutes it doesn’t allow you to work. In this time period it performs its own task and after some time it allows the user to work. This process is called Booting.
During the Booting process computer performs the following tasks:
- It checks whether all its peripheral devices like monitor, mouse, keyboard etc. are working properly ok or not.
- It searches for all the system files or software’s like MS-DOS.sys, IO.sys, COMMAND.com etc. are in the computer or not which helps to run the computer.
- It searches for all the application software’s which works with the help of system software’s are working properly or not.
Booting is divided in two parts:
- Warm Booting (2) Cold Booting
COLD BOOTING:
When we start the computer then for few minutes it does not allow you to work. In this time period computer boots and then it allow us to work. This type of booting is called Cold Booting.
WARM BOOTING:
When we boot the computer without switching off or by pressing the Restart button, then the computer shuts down and again starts. Then that type of booting is called Warm Booting.
HARDWARE :
The term hardware refers to all physical components of a computer system which can be felt and touched. The entire machine is termed as the hardware. For example, monitor, keyboard, printer, mouse, joystick, barcode reader etc. These are the parts or accessories of computer you can touch, feel and see.
WHAT IS DOS:
DOS-Disk Operating System. DOS is a software that controls the hardware of your computer and also runs your programs. It acts as an interface between the user and the computer. DOS tells the computer what to do when you type different commands.
THE PRINTER:
The printer is a device that produces images (numbers, alphabets, graphs, etc.) on paper. After creating a document on the computer, you can send it to the printer for printing its hard-copy which is generally called a printout. The speed of a printer is rated either by pages per minute (ppm) or by characters per second (cps). Printers are available in two models-color and black and white. Color printers are slower and more expensive than black and white printers.
NUMBER SYSTEM:
When we type some letters or words, the computer translates them in numbers as computers can understand only numbers. A computer can understand positional number system where there are only a few symbols called digits and these symbols represent different values depending on the position they occupy in the number.
A value of each digit in a number can be determined using
- The digit.
- The position of the digit in the number.
- The base of the number system (where base is defined as the total number of digits available in the number system).
- Non-Positional Number System
- Positional Number System
POSITIONAL NUMBER SYSTEM:
- Binary Number System
- Octal Number System
- Decimal Number System
- Hexadecimal Number System
Syntax: (1) (101110)2=(?)10 (2) (157)8=(?)10 (3) (14B)16=(?)10 (4) (179)10=(?)2 (5) (556)10=(?)8 (6) (2379)10=(?)16 (7) (101110100)2=(?)8 (8) (731)8=(?)2 (9) (10110111)2=(?)16 (10) (A9)16=(?)2 (11) (564)8=(?)16 (12) (D7)16=(?)8
DOT MATRIX PRINTER:

DMP prints one character at a time as a set of dots produced by the pins on the print head. It uses a nine or twenty-four pin print head. The pins or printing wires are aligned into the shape of the character to be printed before the print head strikes the ribbon. The impact of the strike produces character shapes on paper. The speed of DMP is measured in character per second (CPS). A normal dot matrix printer with nine or twenty-four pin print head can produce output ranging from 50 to 600 characters per second. It produces lot of noise when working. The popular DMPs are Epson, Panasonic, Citizen, Wipro, TVSE and Lexmark. The operating cost for DMP is the lowest among all types of printers.
Inkjet Printer
Inkjet is a non-impact printer and is quiet when working. It sprays ink particles through its nozzle. On leaving the nozzle, the tiny particles of ink get electrically charged. The electrically Computer Fundamentals
charged particles are then guided on to the paper to form appropriate characters. Inkjet printers are as cheap as dot matrix printers are; but their operating costs are far higher than those of dot matrix printers. However, they give much better quality than DMPs. They are available in black and white and colour.The popular brands of inkjet printers are Hewlett-Packard, Epson Stylus and Canon.
Laser Printer
Laser printer is a high-end printer. It is more expensive than inkjet printers and its operating costs are also higher than inkjet printers. It uses the same technology as that of Xerox copier machines and it can produce both character and graphic output. It gives the best quality output. Though expensive, laser printer is becoming increasingly popular.
Daisy Wheel Printer
The daisy wheel printer has a wheel with a number of spokes made up of metal and plastic. Each spoke carries a typeface at the outer end. The wheel rotates until the appropriate character comes under the hammer, which strikes to produce the impression on paper. These wheels are inexpensive and removable. It is slow and produces noise like dot matrix printer; but it gives fine quality output.
Thermal Printer
The thermal printer generates heat to produce the required character shape on specially coated thermal paper. The print head, which carries electric current, burns the aluminum coating on the paper into the character form. It is a quiet printer.
Drum Printer
It is a line printer. It has a drum that rotates at high speed. A set of characters is embossed on the drum. It prints one line of characters at a time. The hammer for a particular character position is activated when that character on the drum passes under it to produce character impression on paper.
Chain Printer
The chain printer works like the drum printer. It consists of a set of typefaces on a chain that rotates at activated to produce one row of characters as it is composed. There is a hammer for each print position. As the characters move around on the chain, the hammer strikes on the opposite side of the print position to produce character impression on paper.
Magnetic Printer
In a magnetic printer, a drum coated with magnetic material captures the image of the page to be printed. These magnetic spots attract dry ink particles, which are then pressurized and transferred to paper to produce output.
Graphic Plotters
Plotters are used for plotting graphs and designs on paper. Architects and designers use plotters to produce blueprints of their designs on paper. It is a specialized output device for preparing computer drawn charts and graphs. The most popular type of plotter is the flat bed device. It plots on paper (or other material) that is spread on a flat bed.
MODEM
The ordinary telephone lines transmit data in analog form. Computers are digital devices and use digital signals for data processing. Modems are used to connect digital computers with telephone lines. Modem at the originating computer modulates the digital signals and at the receiving computer demodulates analog signals. It converts digital signals into analog signals for transmission over telephone lines. At the other end of the channel, the modem converts the analog signals back into digital signals.

Types of Modem
Internal modem: This is built on a card and the card is fixed into a slot on the motherboard of a computer.
External modem: It is external to the system and is plugged into RS 232 or RS 232 C connector for computer communications. Acoustic coupler modem: This is not direct modem. It requires telephone handset as intermediary equipment. Modems come in different speeds like 9.6 kbps, 33.6 kbps etc. The modem speed should at least be equal to bandwidth of the communication channel that sets the maximum size of data that can be sent at a time. If the modem speed is less than the bandwidth, modem will become a bottleneck in communication as it slows down the rate of data transfer.
MS DOS Commands
MS DOS has two types of commands: internal and external. All the internal commands are included in one of the system files, namely, Command.com. Once the computer is booted, the command.com is loaded into main memory of the computer and remains there until the machine is turned off. All the internal commands will be executed when this file is in memory. The external commands require separate modules to be read from the disk for execution and if the module is not there, the command cannot be executed.
Internal Commands
(Note: After typing in the commands, press enter key for
execution) .
1. Dir This command lists the contents of a directory in the hard disk or floppy disk.
Other options are:
Dir/p The Ip option is used to list the contents page wise, one screen at a time.
Dir/w This option lists contents width wise.
Dir [drive] to list the contents of another directory
For example dir a: This command lists all the files in drive A while remaining in drive C.
Dir *. <extension> This lists all files with the extension specified For example dir *.exe lists all files with extension ‘exe’.
Dir *. * This command lists all files in the current directory just like dir command.
Dir com??? * This command lists all files beginning with com and followed by any three characters and with any file extension. Dir ls This lists not only subdirectories in the current directory but also all files within those subdirectories.
2. MD or MKDIR, This command is used to create a directory.
Syntax: MD <DIRECTORY NAME>
For example, if you want to create a directory for employees then give the following command:
MD EMPLOYEE
3. CD This command is to change from one directory to another.
Syntax: CD <SUB DIRECTORY NAME>
4. RD This command removes a subdirectory.
Syntax: RD <SUBDIRECTORY NAME>
Example if the subdirectory SALARY is to be removed, type
RD SALARY
5. COpy This command copies a file from one source file to another file called the destination file.
Syntax: COPY SOURCE FILENAME DESTINATION FILE NAME
Example: COPY XFILE YFILE
This command duplicates XFILE by copying it into another file called YFILE. Now you will have two files with the same contents but different file names.
6. COpy CON This command is used to create Q file in a directory
Syntax: COPY CON <FILE NAME>
Example: To create a file named XFILE type
COpy CON XFILE
Now you can type in the data and to save it, give the command
AZ (Control + Z)
Press enter key as usual.
But if you do not want to save it you can quit without saving by giving the following command instead:
I\Q and pressing enter key. (Control + Q)
7. REN This command renames a file.
Syntax REN <EXISTING FILE NAME> <NEW FILE NAME>
Example: REN XFILE XYFILE
It renames XFILE as XYFILE.
8. DEL This command deletes a file completely.
Syntax: DEL <FILE NAME>
Example: DEL XYFILE.
9. PATH This command is used to set or reset the sequences of directories to be searched for executable files.
Example: PATH=C:\WINDOWS;C:\DOS6;C:\WS7;C:\UTIL
10. PROMPT, This command is used to change the prompt.
$P current default directory
$G > (the greater than sign)
$D system date
$T system time
$V version number
$$ $ sign.
The usual prompt is $P$G that displays C:\> when in root directory.
11. VER This command displays the current version of DOS.
(Example, MS-DOS VERSION 6.20).
12. VOL This command displays the label of the disk in the specified drive.
13. CLS This command clears the screen.
14. DATE This command displays the system date. The system displays current date and asks to enter new
date.
It displays: Current date is Fri 01-04-96
Enter new date (mm-dd-yy):
15. Time This command displays the current time and enables it to be changed if required.
It displays as follows:
Current time is 10:15:40
Enter new time:
16. Type This command displays the contents of a file.
Syntax: Type <filename>
17. Break This command enables or disables the control – break key combination at every system call.
Break on / Break off
External DOS Commands
1. BACKUP This command is used to make back up copies of the mentioned files or all the files in a directory or drive.
2. RESTORE This command restores all files which were backed up using backup command.
Example: RESTORE A: C:
3. TREE This command displays tree structure of the specified directory.
4. ATTRIB This command is used to change the attributes of a file. To hide a file or to make it read only or vice versa.
Syntax: Attrib <filename> [+h] [-h] [+r] [-r]
Example: ATTRIB YFILE -H
This command causes YFILE to be hidden.
5. CHKDSK This command is used to check a disk’s formatted size and available memory space. It
indicates the amount of disk space consumed by system files, data files and bad sectors.
6. DISKCOPYThis command copies entire floppy disk track by track into another disk.
DISKCOPY A: B:
7. COMP This command compares two or more files to see if they are the same.
COMP A:\RAJ C:\RAJESH
8. DISKCOMP This command compares diskettes, It is generally used to verify diskcopy command.
DISKCOMP A: B:
It compares disk in A drive with that in B drive.
9. FASTOPEN It speeds up disk access by maintaining a memory resident table of the most recently used file and directory names with their memory locations.
Syntax: FASTOPEN [DRIVE]: NUMBER OF FILES
Example: FASTOPEN C:50 This instructs DOS to remember the location of the last 50 directories or files which were accessed recently from drive C:
10. FORMAT This command is used to format a new disk.
FORMAT A:
This formats a disk in A drive.
FORMAT A: /S This formats and copies system files on to the disk in A drive.
11. PRINT This command is used to print a file or a group of files.
Syntax PRINT <FILENAME>
Examples: PRINT STUDENT. DAT (To print a file named student.dat)
PRINT *. DAT (To print a group of files with file extension DAT).
12. RECOVER This command recovers damaged file ( that is file with bad sectors). Syntax RECOVER <FILENAME>
13. REPLACE This command is used to update a set of files in one directory or drive with another set of
similarly named files in another directory or drive.
Syntax REPLACE B:\*.* C:\EMPLOYEE
This command copies all files in root directory in B drive to subdirectory EMPLOYEE in Drive C:-
14. LABEL This command is used to add or delete or modify the volume label of floppy or hard disk.
LABEL A: DCMS
DCMS becomes the label of the disk in drive A.
MULTIMEDIA INTRODUCTION
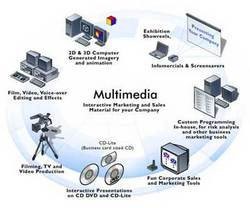
Multimedia computing and communications are attracting a lot of interest these days. It is a term generally used to mean any application or technology that is used to manipulate text, audio, video, images and graphics. It can provide certain amount of interactivity to users. It is used extensively in education, business advertising, publishing, website design, entertainment and video games. The increasing popularity of multimedia opens up large number of career opportunities for the youth like video editor, Visual effects designer, Animator, Cartoon Animator, Software editor, Software mixer, Audio and Video Specialist, Visual effects Professional, Author, Script Writer, Set Designer, Audio Editor, 3D Animator, Character Animator, and Special Effects Manager.
Meaning of Multimedia
The tem ‘multimedia’ means use of multiple media for communicating information. The common media used include text, graphics, animation, audio and video. Use of two or more of these media for presenting information is, therefore, called multimedia presentation. Multimedia software can handle different types of data and hence it enhances the effectiveness of communication. In addition to different media mentioned above, the term ‘media’ can also be understood in terms of data representation medium like ASCII and EBCDIC, image representation through JPEG and MPEG formats, presentation medium like paper, screen
and speaker, data storage medium like floppy disk, hard disk and CD-ROM. The medium may also mean transmission medium like wired or wireless networks.
MULTIMEDIA COMPONENTS
The multimedia. components include text, graphics, animation, audio and video. Two or more of these components are combined into presentations or creations for desired effects with the target audience.
Text
Text contains d.ata in alphanumeric form. Hardware required for text precessing requires keyboard, optical scanners, display screens and printers. The software required for text processing includes word processors for editing and formatting text with different fonts, hypertext features etc.
Animation

Computer animation is the use of graphic tools to create visual effects. The visual effects can be in the form of changes in shape, color, lighting, position etc. Computer animation gives movement to objects. Graphic software is used to create such objects. Computer animation is used in cartoon films, electronic advertisements, video games and virtual reality applications. Indian mythological characters like Hanuman, Ram and Lakshman are being recreated in cartoon films with animation. Animation application areas include movies, television production, product promotions, computer based training and education, graphics in publishing, web design, virtual reality for simulations, engineering, advertising and fashion design.
Audio
Audio is an important component of multimedia. Audio or sound is produced by vibration of matter. As the matter vibrates, variations in air pressure around it is propagated in a wave like motion. Audio techniques deal with processing of these sound ·waves. Audio component deals with synthesizing, recording and play back of audio. It is extensively used in education and training software. Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) is another technology that helps in enhancing audio special effects.
Video
It is a sequence of moving images of a real life situation. Properties of human eye and neuronal processing are critical factors in video systems. With 30 frames per second, video motion appears smooth and continuous.
Images
Image is a spatial representation of an object. Images are represented in computer with a matrix of numeric values to manipulate pixels. That is, digital images are stored as two dimensional array of values. Each value represents the data associated with a pixel.
Graphics
Computer graphics deal with the generation and manipulation of digital objects. The objects may be drawn with graphic software or scanned-in with digital scanners. The objects can be animated by controlling speed, portion of the total scene in view etc.
APPLICATIONS OF MULTIMEDIA
The flexibility of using different types of data for communication makes multimedia especially suitable for some applications like education, training, entertainment, advertisement, cartoon movies, video games etc.
Multimedia in education
Multimedia is particularly suitable for developing digital content for education and presenting it attractively. The students can view text in a text box which can be scrawled up and down. Simultaneously, they can listen to audio that reads out the text. Drawings and animation are used to make objects appear real life with movements.
Multimedia in Training
Another important use of multimedia is in training. Voice, text, images, movies and animation are used in developing training material. The trainees can interact with the software. Multimedia makes the presentation visually attractive and stimulates thinking.
Special effects in movies
Multimedia technology is used in movies for special effects. Movies with multimedia effects are much in demand. Jurassic park, Spiderman, Harry Potter and Titanic are examples where multimedia helps in creating special effects.
Multimedia on the web
With multimedia, emails, instant messaging and websites can be made much more attractive and lively. It can be used to enrich the content and provide interactivity for the users. It can attract more visitors to the site. The Web has become the standard medium for global communications.
Multimedia in Printing and Publishing
Multimedia is used in printing and publishing to improve quality of print and layouts. With a variety of font designs, colors, graphics etc. multimedia can be used to enhance quality of printing and publishing.
Multimedia in Designing
| 3D MAX |

Computer graphics and 3-D object modeling help designing in creating designs of objects with ease. A range of colors, forms, textures and tones enable them to experiment with designs. Multimedia, thus, enables designers to give shape to their imagination virtually.
SUMMARY
Multimedia software can handle different types of data simultaneously and this capability makes it extremely useful for attractive presentation of information. It makes any presentation rich with audio, video and animation. Its use is growing very rapidly and it opens up large number of career opportunities for creative IT professionals. the multimedia professionals are in short supply worldwide.
WHAT IS THE INTERNET? THE WEB? A HOMEPAGE?
The Internet started out as part of the National Science Foundation (NSF) and part of the ARPA (believe it or not, the US Army research network). These systems lost funding and were sold to companies (deregulated in 1987). Computers can be connected together into a network and can share files between each other. The Internet is a “super” network that connects the entire world together. (If you would like to know more, goto “http://www.yahoo.com/Computers_and_Internet/Internet/History/”.)

The “web” is a part of this network that links documents haphazardly together (based on interest of the author). The web has an addressing system which is called a URL (Uniform Resource Locator). The URL is like an address to someone’s house, but in this case, it refers to a file or resource available on the web. Whenever you click on a highlighted term in a webpage (a document displayed by your browser), you are linking over to a new document using the URL.
A homepage is a document on the web that an author designed about him/herself. It can also be a summary of a company. Designing Webpages have become dramatically easier over the past few months. Netscape includes a webpage editor as part of their “3.0 Gold” version.
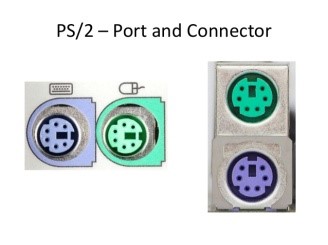
PS/2 Port
Used for old computer keyboard and mouse also called mouse port Most of the old computers provide two PS/2 port, each for mouse and keyboard Also known as IEEE 1284-compliant Centronics port.
Universal Serial Bus (or USB) Port

It can connect all kinds of external USB devices such as external hard disk, printer, scanner, mouse, keyboard etc. It was introduced in 1997. Most of the computers provide two USB ports as minimum. Data travels at 12 megabits per seconds USB compliant devices can get power from a USB port.
VGA Port

Connects monitor to a computer’s video card. Has 15 holes. Similar to serial port connector but serial port connector has pins, it has holes.
What is a Computer Network?
A computer network is a system in which multiple computers are connected to each other to share information and resources.
Characteristics of a computer network
- Share Resources from one computer to another
- Create files and store them in one computer, access those files from the other computer(s) connected over the network
- Connect a printer, scanner, or a fax machine to one computer within the network and let other computers of the network use the machines available over network.
- Following is the list of hardware’s required to setup a computer network.
- Network Cables
- Distributors
- Routers
- Internal Network Cards
- External Network Cards
LOGIC GATE:
A logic gate is an elementary building block of a digital circuit. Most logic gates have two inputs and one output. At any given moment, every terminal is in one of the two binary conditions low (0) or high (1), represented by different voltage levels. The logic state of a terminal can, and generally does, change often, as the circuit processes data. In most logic gates, the low state is approximately zero volts (0 V), while the high state is approximately zero volts (0 V), while the high state is approximately five volts positive (+5 V).
There are seven basic logic gates: AND, OR, XOR, NOT, NAND, NOR and XNOR.
AND gate:
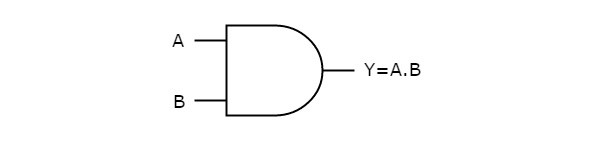
The AND gate is so named because, if 0 is called “false” and 1 is called “true”, the gate acts in the same way as the logical “and” operator. The following illustration and table show the circuit symbol and logic combinations for an AND gate. (In the symbol, the input terminals are at left and the output terminal is at right.)
Rules: The output is “true” when both inputs are “true”, Otherwise, the output is “false”.
| AND gate : 2X1 SERIES -:- 22=4 3X1 SERIES -:- 23=8 4X1 SERIES -:- 24=16 5X1 SERIES -:- 25=32 |
| Truth Table 2×1 Series | ||
| INUT A | INPUT B | OUTPUT f=A.B |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
OR GATE:
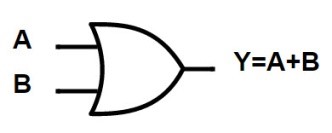
The OR gate gets its name from the fact that it behaves after the fashion of the logical inclusive “Or.”
Rules: The output is “true” if either or both of the inputs are “true.” If both inputs are “false,” then the output is “false.”
| OR gate : 2X1 SERIES -:- 22=4 3X1 SERIES -:- 23=8 4X1 SERIES -:- 24=16 5X1 SERIES -:- 25=32 |
| Truth Table 2×1 Series | ||
| INUT A | INPUT B | OUTPUT f=A+B |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
NOT GATE:
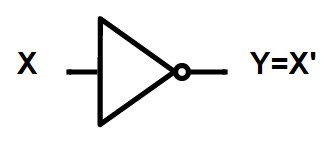
A logical inverter, sometimes called a NOT gate to differentiate it from other types of electronic inverter devices, has only one input. It reverses the logic state.
| Truth Table | |
| INPUT | OUTPUT |
| 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 |
ASCII – American standard Code for Information Interchange.
DBMS – Data Base Management System
A.B.C – Atanosoft Berry Computer
GUI – Graphical User Interface
MIS – Management Information System
E-mail – Electronic Mail
DTP – Desk Top Publishing
EFT – Electronic Fund Transfer
ATM – Automated Teller Machine
VDU – Visual Display Unit
OCR – Optical Character Reader or Scanner
OMR – Optical Mark reader
SSIC – Small Scale Integrated Circuit
KIPS – Knowledge Information Process System
UNIVAC – Universal Accounting Company / Universal Automatic Computer
MICR – Magnetic Ink Character Reader
LCD – Liquid Crystal Display
TFT – Thin Film Transistor
CD-ROM – Compact Disk Read Only Memory
EEPROM – Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
DRAM – Dynamic Random Access Memory
SRAM – Static Random Access Memory
M.U – Memory Unit
ALU – Arithmetic and Logic Unit
CU – Control Unit
CPU –Central Processing Unit
VLSIC – Very Large Scale Integrated Circuit
IBM – International Business Machine
EDSAC – Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Computer
EDVAC – Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer
ENIAC – Electronic Numerical Integrator And Calculator
RAM – Random Access Memory
ROM – Read Only Memory
MD – Make Directory
CD – Change Directory
RGB – Red Green Blue
CMYK – Cyan Magenta Yellow Keycolor (Black)
JPEG – Joint Photographic Experts Group
BIT – Binary Digit
PNG – Portable Network Graphics
BMP – Bitmap Picture
CRT – Cathode Ray Tube
LCD – Liquid Crystal Display
MODEM – Modulator-Demodulator
WWW – World Wide Web
HTTP – Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
HTML – Hyper Text Markup Language
MOUSE – Mechanically Operated User Serial Engine
MS-DOS – Microsoft Disk Operating System
URL – Uniform Resource Locator
INTERNET – Inter Connected Network
FTP – File Transfer Protocol
STMP – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
SMPS – Switch Mode Power Supply
POST – Power On Self Test
BIOS – Basic Input Output System
ISDN – Integrated Services Digital Network
ISP – Internet Service Provider
VSNL – Videsh Sunchar Nigam Ltd.
ARPANET – Advanced Research Project Administration Network
BCD – Binary Coded Decimal
LSB – Least Significant Bit
MSB – Most Significant Bit
SQL – Structured Query Language
OOP – Object Oriented Programming
CPU – Central Processing Unit
GUI – Graphical User Interface
DEMS – Digital Electronic Management System.
VIRUS – Vital Information Resources Under Seize
JVM – Java Virtual Machine
HLLS – High Level Languages
TCP/IP – Transfer Control Protocol / Internet Protocol
RDBMS – Relation Database Management System
DOA – Date of Admission
LAN – Local Area Networking
MAN – Metropolitan Area Networking
WAN – Wide Area Networking
PNG – Portable Network Graphics
TIFF – Tagged Image File Format
RTF – Rich Text Format
CSS – Cascading Style Sheet
PAN-Permanent Account Number
PDF-Portable Document Format
SIM-Subscriber Identity Module
IFSC-Indian Financial System Code
GST-Goods Service Tax
VAT-Value Added Tax
OTP-One Time Password
EPIC-Electrors Photo Identity
ATM-Automated Teller Machine
Extension File :
Note Pad Application : *.TXT
Word Pad Application : *.RTF
Ms-Paint Application : *.BMP
Ms-Office Word : *.DOC
Ms-Office Excel : *.XLS
Ms-Office Power Point : *.PPT
Ms-Office Access : *.DMP
Photoshop : *.PSD
Corel Draw : *.CDR
Page Maker : *.PMD
Illustrator : *.AI
Flash : *.FLA
Freehand : *.FH
3D MAX : *.MA
Shortcut Key
- Ctrl+A = Select All
- Ctrl+B = Bold
- Ctrl+C = Copy
- Ctrl+D = Font / Duplicate
- Ctrl+E = Center Alignment
- Ctrl+F = Find
- Ctrl+G = GoTo
- Ctrl+H = Replace
- Ctrl+I = Italic
- Ctrl+J = Justify Alignment
- Ctrl+K = Hyperlink
- Ctrl+L = Left Alignment
- Ctrl+M = One Tab Stroke / New Slide (Power Point)
- Ctrl+N = New Page
- Ctrl+O = Open
- Ctrl+P =Print
- Ctrl+Q = Convert to Curve
- Ctrl+R= Rotate / Right Alignment
- Ctrl+S = Save
- Ctrl+T = Toolbox
- Ctrl+U = Underline
- Ctrl+V = Paste
- Ctrl+W = Skew
- Ctrl+X= Cut
- Ctrl+Y = Redo
- Ctrl+Z = Undo
- Ctrl+] = Font Size increase
- Ctrl+[ = Font Size decrease
- Alt+F4 = Shut Down
Managing Files and Folders(Windows Explorer)
You can manage all your files and folders through Windows Explorer. You will be surprised to know that the explorer can carry out so many important functions.
- It can help you to start programs and open documents.
- It can copy, create, move and delete files and folders.
- You may see and change the files/folders structure of your disk.
- Even if you want to change the properties of files, you may do so.
Recycle Bin :

The Recycle Bin actually helps you to recycle your files. This allows you to recover your deleted files. From Recycle Bin, you can also delete files permanently. To delete or restore files from the recycle bin, double click the Recycle Bin icon at the desktop. Select the files to be deleted and press delete. To bring this file back into function, open Recycle Bin, select the File and click Restore option. This will restore the file.
What is File?
A computer file is a unit of information. It holds a document such as letter or text, group of database records like your class, name, roll number, results etc. or a program. File is also used to store texts, graphics, pictures, drawings, sound etc. Hence, we can say computer file is similar to an office file kept in a filing cabinet or almirah containing various information. But it is necessary that each file when stored in a computer to be given a name. You must give different names to different files. It helps you to locate the same for future use quickly.
What is a Folder?
A folder contains collection of files. Hence, a folder contains many files and you can easily find and work with the related files. Sometimes, folders are also referred to as sub-directories.
Desktop:
The large, background area of the Windows screen. You can customize the desktop by adding shortcuts to your favourite programs, documents and printers. You can also change the look of the desktop to fit your mood and personality.
Icons :
These are the small graphical symbols that represent applications such as word processing or Internet Explorer in Windows. Icons are the minimized form of windows represented by graphical pictures.
Wi-Fi :
Wi-Fi stands for Wirless Fidelity which helps you connect to Internet without direct line from your computer to ISP(Internet Service Provider). For Wi-Fi, the system needs-

- A broadband Internet connection
- A router to connect computer to ISP where it relays your Internet connection.
- A smartphone, laptop or desktop having wireless Internet card. An external wireless adaptor can also be deployed.
With wi-fi there are some security hazards. In wi-fi system the most dangerous fear is that it can easily be hacked. If it is hacked, your data can be stolen. So before putting wi-fi on your computer at home, use some security system for your computer.


Very good update educational blogging webpage side.
Please observe this blogging side
Very good computer basic concepts knowledge of everything so I like this blogging website